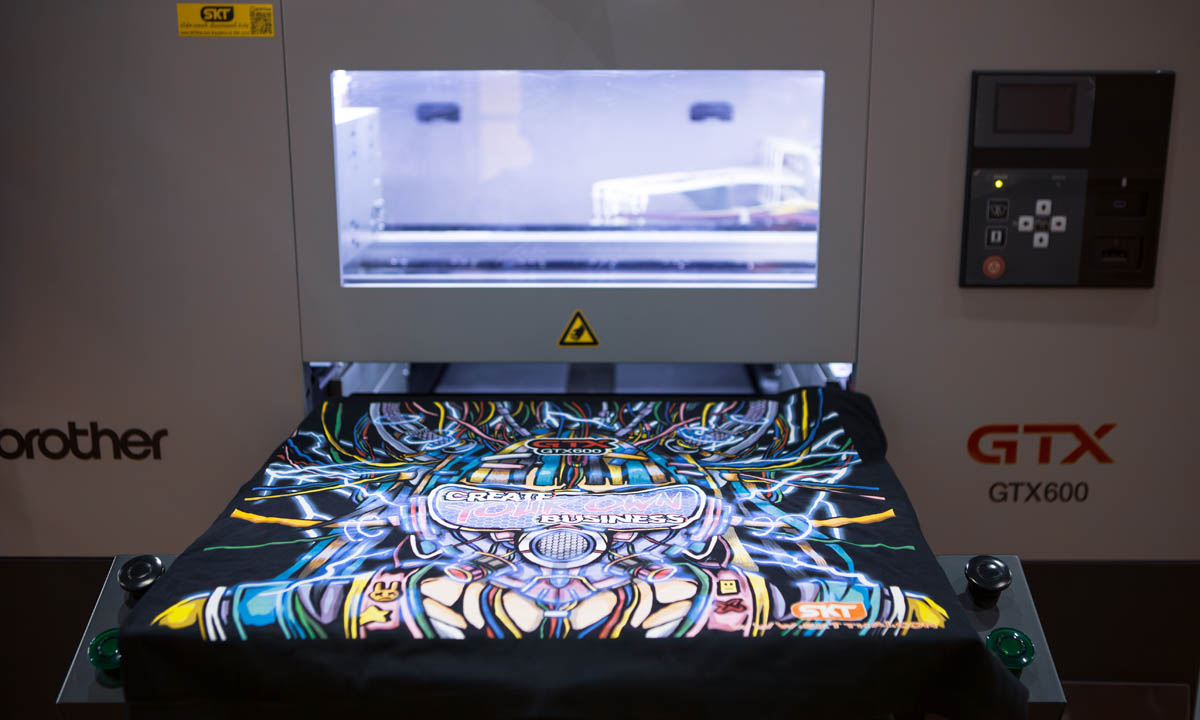
When it comes to apparel decoration, the options are plentiful. From screen printing to embroidery, the garment decoration industry boasts a myriad of techniques. Yet, one method stands out for its sustainability — direct-to-garment (DTG) printing. In today’s world, sustainability is more than just a buzzword — it’s essential. The textile and garment sector finds itself at a pivotal point in its environmental impact efforts. Traditional decoration methods often miss the mark on sustainability. However, DTG printing offers a beacon of hope, providing a greener alternative that seamlessly merges print quality with eco-consciousness.
Understanding DTG printing
DTG printing is a relatively straightforward process. It involves using specialized inkjet technology to print designs directly onto fabric or preassembled garments. This method contrasts sharply with traditional analog printing techniques, which often require multiple steps and Earth resources. DTG’s simplicity translates into various environmental benefits, making it a go-to choice for eco-conscious brands and consumers.
The versatility of DTG printing is one of its standout features. It’s perfect for small batch production, custom orders, multi-colored designs, and intricate designs that require fine details. Thanks to its digital foundation, DTG is ideal for print-on-demand, which means garments can be produced as they are ordered. This drastically reduces overproduction and the associated waste. DTG users can print one or many garments with multi-colors and patterns without the upfront cost and material waste of other decoration methods.
Advantages of DTG printing
Water efficiency: DTG printing requires no additional water for the printing process, unlike screen printing, where a single production facility can consume hundreds of gallons of water annually. This represents a groundbreaking advancement, especially in an era where water scarcity is becoming increasingly problematic.
Minimal waste: Traditional printing methods often result in significant waste, whether it’s excess ink or leftover materials. DTG, conversely, uses the precise amount of ink needed for each design, leading to virtually zero waste.
Energy consumption: DTG printers are typically more energy-efficient than their traditional counterparts. By reducing the amount of electricity required for each print run, DTG contributes to lower carbon emissions, further boosting its sustainability credentials.
Eco-friendly ink: Most DTG inks have no or minimal levels of toxic substances. DTG printers use water-based inks that are less harmful to the environment compared to the chemical-laden ones used in traditional printing.
No pre- or post-materials: Unlike screen printing or heat transfer methods, the DTG process produces no waste and requires no post-production cleanup. This not only makes it an environmentally friendly option but also saves time and reduces labor costs.
Comparing other decoration methods:
While DTG shines in its sustainability, it’s crucial to understand how it stacks up to the other most popular decoration methods.
Screen printing
Screen printing is one of the oldest and most widely used methods for decorating apparel. However, it has several drawbacks when it comes to sustainability:
Water usage: Screen printing involves extensive water use, from developing and reclaiming screens to cleaning ink. This makes it less eco-friendly compared to DTG.
Chemical exposure: The inks and solvents used in the screen-printing process often contain some level of harmful chemicals, posing risks to both the environment and human health.
Production drawbacks: Screen printing requires a separate screen for each color printed. Screens require a tremendous amount of water when processed for production and also in post-production clean up. There can also be harmful chemicals used in the production of screens. Further, screen printing uses quite a few suspect chemicals, and generates landfill waste, during the production process.
Space requirements: Screen printing requires several large production machines, necessitating ample space and resulting in higher energy demands for both the construction and maintenance of buildings. These machines also demand significant amounts of electricity to function.
Direct-to-film printing
Direct-to-film (DTF) heat transfer techniques involve digital printing onto a plastic film, coating the wet printing ink with special powder, curing the printed and coated ink in a dryer, and then using heat and pressure to apply designs onto fabric. While this method has its merits, it also falls short in certain areas:
Plastic waste: Most DTF heat transfers are printed on petroleum-based plastic materials made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a highly polluting microplastic. These transfers contribute to landfill waste since the carrier sheet is single-use and is rarely recycled. There have been some advances in using recycled papers with a PET coating for the process, but they too are still a one-time use and could eventually end up in the trash.
Post-processing powder: The DTF transfer necessitates a petroleum-based, finely ground polyester powder TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) coating over the printed ink, enabling it to adhere effectively to the fabric. However, there are concerns regarding the overall safety of this powder. If the post-production residue powder is disposed of improperly, or if residue remains post-application, it can end up in groundwater and contribute to the ongoing global issue of microplastic contamination.
Green technology
DTG printing aligns with the principles of green technology by integrating innovations that prioritize environmental health. The use of biodegradable, water-based inks ensures minimal ecological impact. Furthermore, many DTG printers are designed with energy efficiency in mind, reducing the carbon footprint associated with garment production. The shift towards sustainable textile production is further supported by the ability to use organic and recycled fabrics with DTG printing, promoting a circular economy within the industry.
Why DTG is the most sustainable choice
Given the drawbacks of other decoration methods, DTG printing stands out as the most sustainable option available today. Its eco-friendly inks, water efficiency, minimal waste production, and low energy consumption make it an environmentally responsible choice for businesses and consumers alike.
In a world increasingly aware of its ecological footprint, making sustainable choices is no longer optional — it’s imperative. By opting for DTG printing, companies can significantly reduce their environmental impact while delivering high-quality, vibrant designs. This aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products and practices, making DTG not just an ethical choice but a smart business decision as well.
The future of apparel decoration lies in sustainable practices, and DTG printing is leading the charge. Its advantages over traditional methods are clear, making it the ideal choice for those looking to combine quality with environmental responsibility.
Let’s make a conscious effort to choose methods that protect our planet. With DTG printing, we can still create beautiful, lasting designs while safeguarding the environment for future generations.